18 Common Restaurant Health Code Violations and How to Prevent Them
Health violations in restaurants can tarnish a reputation faster than you can say “health inspection.” Restaurants with health code violations not only risk losing customers but could also face hefty fines or even closure. To help restaurant owners and managers stay compliant, we’ve outlined 18 common violations, why they happen, and actionable steps to prevent them.
Let’s look at what these violations are and what you can do to keep your kitchen compliant and your customers safe.
1. Cross-Contamination
The Problem: Bacteria or allergens transfer between raw and cooked foods or through unclean surfaces, utensils, and improper handling.
Why It Happens:
- Improper food storage (e.g., raw chicken above produce).
- Using the same cutting boards or utensils for raw and cooked items.
How to Prevent It:
- Use color-coded equipment for different food types.
- Train staff to sanitize surfaces and utensils between uses.
- Store raw ingredients on lower shelves to prevent drips onto ready-to-eat foods.
Pro Tip: Schedule routine audits to ensure sanitation protocols are followed.
2. Bare-Hand Contact with Ready-to-Eat Food
The Problem: Direct hand contact with foods like salads or sandwiches increases the risk of contamination.
Why It Happens:
- Neglecting to wear gloves or use utensils.
- Poor awareness of food safety regulations.
How to Prevent It:
- Provide gloves and utensils for food handling.
- Emphasize handwashing and regular glove changes.
Pro Tip: Post visual guidelines at prep stations to ensure compliance.
3. Improper Cooking Temperatures
The Problem: Undercooking meats or other items can result in harmful bacteria, like E. coli, thriving in meals.
Why It Happens:
- Relying on guesswork instead of thermometers.
- Uncalibrated cooking equipment.
How to Prevent It:
- Train staff to use and read thermometers correctly.
- Regularly calibrate cooking appliances to ensure consistent results.
Pro Tip: Display cooking temperature charts in visible areas for quick reference.
4. Failure to Rapidly Cool or Reheat Foods
The Problem: Foods staying in the “danger zone” (40°F–140°F) for too long create perfect conditions for bacterial growth.
Why It Happens:
- Improper use of cooling equipment.
- Lack of awareness about cooling and reheating protocols.
How to Prevent It:
- Use shallow containers for cooling.
- Invest in equipment like blast chillers for large batches.
- Log and monitor cooling and reheating times.
Pro Tip: Designate a staff member to oversee cooling processes during shifts.
5. Poor Handwashing Practices
The Problem: Insufficient handwashing spreads germs and contaminants throughout the kitchen.
Why It Happens:
- Lack of training or enforcement of handwashing policies.
- Poorly maintained or inaccessible handwashing stations.
How to Prevent It:
- Educate staff about the importance of handwashing.
- Ensure sinks are stocked with soap, hot water, and paper towels.
Pro Tip: Set up automated timers near sinks as reminders for thorough washing.
6. Improper Food Storage Temperatures
The Problem: Incorrect refrigeration or freezing leads to spoilage and bacterial contamination.
Why It Happens:
- Malfunctioning equipment.
- Overcrowded refrigeration units obstructing airflow.
How to Prevent It:
- Check equipment temperatures daily.
- Space out stored items for proper circulation.
Pro Tip: Use digital monitors with alerts for temperature deviations.
7. Pest Infestation
The Problem: Pests spread diseases and contaminate food and surfaces.
Why It Happens:
- Poor waste management.
- Gaps in building structures allowing access.
How to Prevent It:
- Seal cracks and clean all spills promptly.
- Schedule professional pest control inspections.
Pro Tip: Use ultrasonic pest repellents for additional protection.
8. Expired Food Items
The Problem: Serving spoiled or outdated food compromises safety and taste.
Why It Happens:
- Disorganized storage practices.
- Lack of inventory rotation.
How to Prevent It:
- Implement a “first-in, first-out” inventory system.
- Train staff to regularly check and discard expired items.
Pro Tip: Label all perishable goods with expiration dates and use-by dates.
9. Dirty Kitchen Equipment
The Problem: Neglected equipment harbors bacteria and poses a hygiene risk.
Why It Happens:
- Overlooked or inconsistent cleaning schedules.
- Lack of understanding about cleaning requirements.
How to Prevent It:
- Create a thorough cleaning checklist for all equipment.
- Train staff to disassemble and clean machinery correctly.
Pro Tip: Use cleaning tags to indicate when equipment was last sanitized.
10. Improper Dishwashing Techniques
The Problem: Failing to properly sanitize dishes and utensils can result in contamination, posing health risks to consumers.
Why It Happens:
- Using the wrong sanitizing solutions or temperature.
- Inconsistent dishwashing procedures.
How to Prevent It:
- Use a three-compartment sink or high-temperature dishwasher.
- Test sanitizer levels regularly to confirm effectiveness.
- Train staff on proper dishwashing procedures.
Pro Tip: Digitize dishwashing records to ensure consistent compliance with sanitization standards.
11. Cluttered or Dirty Floors
The Problem: Spills and clutter on kitchen floors increase the risk of accidents and contamination.
Why It Happens:
- Failure to clean up spills promptly.
- Lack of organization in kitchen storage areas.
How to Prevent It:
- Sweep and mop floors regularly.
- Clean spills immediately and store items off the ground.
- Use non-slip mats in high-traffic areas.
Pro Tip: Assign designated cleaning zones to ensure consistency in maintenance.
12. Inadequate Food Protection
The Problem: Leaving foods uncovered or improperly stored can lead to contamination and spoilage.
Why It Happens:
- Improper storage methods or containers.
- Failure to cover food properly or label it clearly.
How to Prevent It:
- Cover food with lids or wraps and label containers clearly.
- Organize storage areas to minimize exposure.
- Inspect containers for damage or leaks regularly.
Pro Tip: Assign “food safety leads” for every shift to verify that food storage standards are met.
13. Improper Employee Hygiene
The Problem: Poor personal hygiene among employees can lead to contamination and health risks.
Why It Happens:
- Employees neglecting hygiene protocols or not following proper handwashing procedures.
- Lack of supervision or enforcement of hygiene rules.
How to Prevent It:
- Set clear hygiene standards, including clean uniforms and hairnets.
- Conduct regular hygiene audits and provide feedback.
- Encourage accountability through team rewards for compliance.
Pro Tip: Offer rewards for consistent adherence to hygiene protocols to foster a culture of accountability.
14. Unapproved Food Sources
The Problem: Using food from unverified or unapproved suppliers can compromise food safety and quality.
Why It Happens:
- Purchasing ingredients from non-licensed vendors.
- Failure to verify supplier credentials.
How to Prevent It:
- Source food only from licensed vendors.
- Verify supplier credentials regularly.
- Maintain records of certifications and quality checks.
Pro Tip: Partner with local suppliers for fresher ingredients and more traceable sourcing.
15. Unclean Restrooms
The Problem: Filthy restrooms reflect poorly on overall cleanliness and can affect customer perception.
Why It Happens:
- Failure to clean restrooms regularly.
- Insufficient supplies like soap or paper towels.
How to Prevent It:
- Clean restrooms multiple times daily.
- Restock soap, paper towels, and sanitizers regularly.
- Conduct periodic restroom inspections for maintenance issues.
Pro Tip: Use a restroom cleanliness tracker to ensure accountability during busy shifts.
16. Grease Buildup in Exhaust Systems
The Problem: Accumulating grease in kitchen exhaust systems poses a fire hazard and affects air quality.
Why It Happens:
- Lack of regular maintenance or cleaning of exhaust systems.
- Excessive grease production during cooking.
How to Prevent It:
- Schedule professional exhaust cleaning regularly.
- Conduct visual inspections of exhaust systems weekly.
- Educate staff on minimizing grease production during cooking.
Pro Tip: Equip exhaust systems with filters designed to reduce grease buildup more effectively.
17. Failure to Properly Label Allergens
The Problem: Not informing customers of potential allergens in dishes can lead to severe allergic reactions, which can be life-threatening.
Why It Happens:
- Lack of allergen tracking or labeling practices.
- Inadequate communication between kitchen staff and waitstaff about allergens.
How to Prevent It:
- Clearly mark allergens on menus and food containers.
- Train staff on handling allergy-related requests.
- Maintain an updated allergen tracking system.
Pro Tip: Use digital menu boards for quick allergen updates.
18. Inadequate Training for Employees
The Problem: Staff who are unaware of food safety protocols are more likely to commit health code violations.
Why It Happens:
- Lack of structured training programs.
- Limited staff knowledge about health code requirements.
How to Prevent It:
- Conduct regular training on food safety and hygiene.
- Use hands-on demonstrations for key processes.
- Evaluate staff understanding with quizzes and practical tests.
Pro Tip: Incorporate gamified e-learning modules to make training more engaging and effective.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Why Health Codes Matter?
Health codes are the backbone of food safety, designed to protect the public and uphold standards in the restaurant industry. By enforcing guidelines on hygiene, food handling, and preparation, they minimize risks and ensure safe dining experiences. Here’s why adhering to health codes is essential:
- Public Health Protection: Health codes establish standards to prevent contamination and the spread of foodborne illnesses, safeguarding customer health.
- Regulatory Compliance: Restaurants must adhere to these codes, which cover food storage, preparation, and employee hygiene, to avoid legal penalties.
- Enforcement Actions: Violations can result in fines, mandatory follow-up inspections, or even temporary closure by the health department until issues are corrected.
- Reputation Management: Health code violations can damage a restaurant’s reputation, leading to a loss of consumer trust and decreased patronage.
By following health codes, restaurants can protect their patrons from health risks and maintain a successful business operation.
How KNOW Can Help Avoid Restaurant Health Code Violations?
Running a restaurant means juggling countless tasks while ensuring compliance with food safety and health codes. With so many moving parts, even the most diligent managers can miss something. This is where KNOW comes in, acting as your digital restaurant operations assistant.
From compliance to staff management, KNOW offers a set of solutions designed to help you meet regulatory requirements, improve efficiency, and provide a safe environment for both your customers and staff. Here’s how KNOW can support your restaurant in key areas:
1. Ensure Food Safety and Hygiene Standards
KNOW helps you set up customizable checklists and automates reminders for hygiene practices, ensuring your kitchen consistently meets food safety standards. Real-time tracking lets you stay on top of sanitation tasks and monitor compliance with health codes.
2. Streamline Staff Training and Onboarding
With KNOW, you can provide your team with comprehensive training modules and track their progress. New hires can get up to speed quickly with bite-sized learning journeys, while ongoing training ensures everyone stays updated on food safety protocols.

3. Manage Checklists and Daily Tasks
KNOW makes it easy to assign tasks, set reminders, and monitor progress to ensure that daily operations are always aligned with food safety guidelines. You can create tailored checklists for every shift, so nothing falls through the cracks.
4. Track and Resolve Equipment and Facility Issues
KNOW helps you log maintenance issues in real time, track repairs, and schedule regular upkeep. Whether it’s pest control, equipment malfunctions, or fire safety concerns, KNOW helps you resolve problems quickly before they impact food safety or operations.
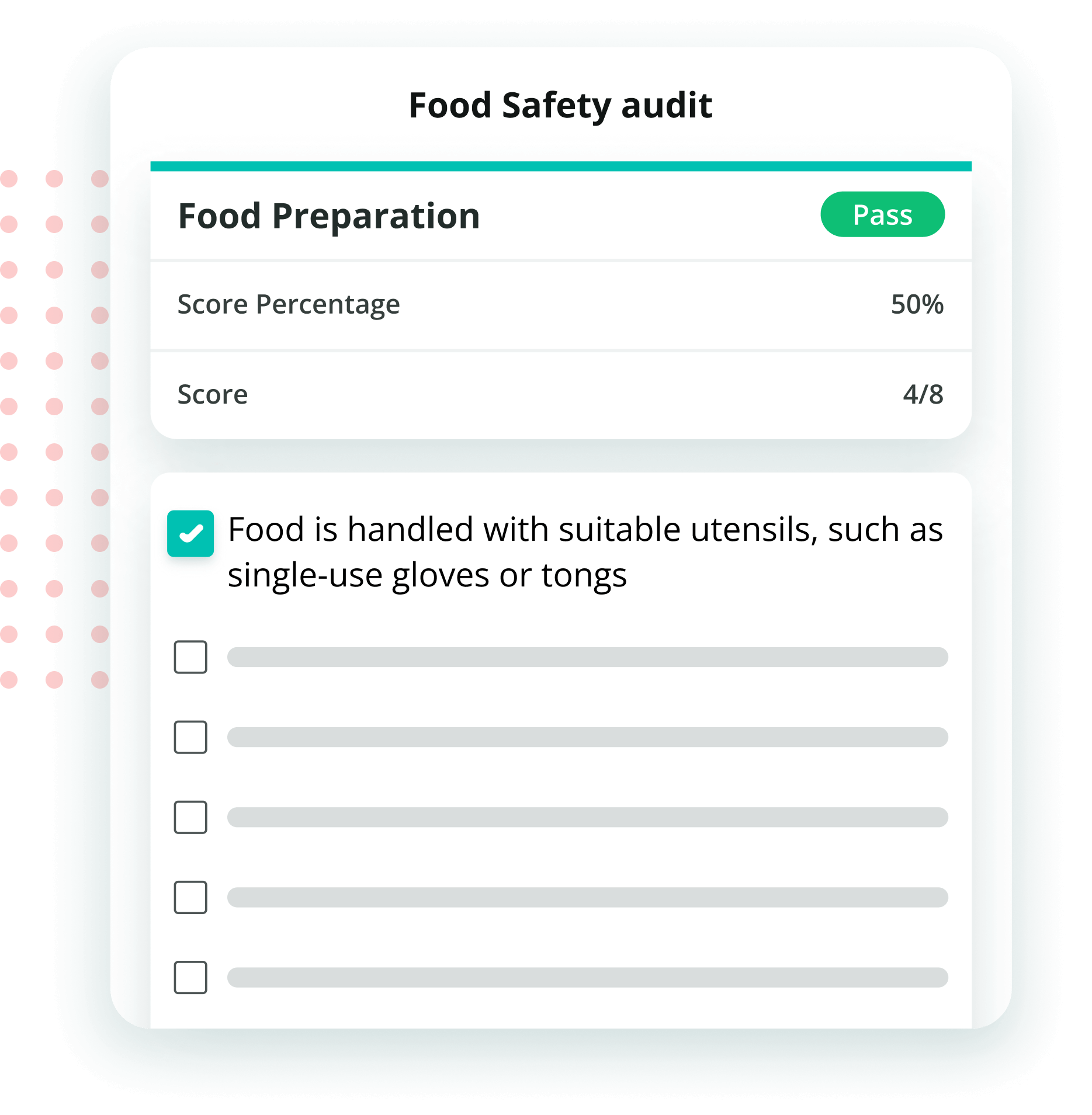
5. Simplify Health Audits and Compliance
With KNOW, audits become a streamlined process. All your food safety checks, sanitation logs, and compliance data are digitized and stored in one place. This ensures you’re always prepared for inspections and can quickly address any compliance gaps.
6. Enhance Scheduling and Attendance Management
KNOW lets you create efficient work schedules, track attendance, and ensure proper staffing levels during peak times. It also helps you stay compliant with labor laws by managing shift hours, breaks, and overtime accurately.
7. Digitize Documentation and Reporting
Forget the hassle of paper trails. KNOW digitizes all documentation and generates easy-to-access reports for audits, inspections, and daily tasks. With centralized, up-to-date records, you’ll have the data you need at your fingertips, saving you time and reducing errors.
Final Thoughts
Managing food safety, hygiene, and daily operations can be overwhelming, but with KNOW, you have a powerful tool to streamline your processes and ensure compliance with ease. From staff training to task management and scheduling, KNOW helps your restaurant stay organized, efficient, and ready for audits, inspections, or any challenge that comes your way.
Ready to simplify your operations and enhance your restaurant’s efficiency? Book a demo today and see how KNOW can transform the way you manage your food safety and team operations. Let us help you focus on what truly matters—serving great food and delivering excellent customer experiences.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. Who is responsible for creating health codes?
Health codes are typically created and enforced by local, state, or national health departments. These agencies establish regulations to ensure food safety, sanitation, and public health in the restaurant industry.
2. Who ensures restaurants comply with health codes?
Health inspectors from local or state health departments are tasked with ensuring restaurants comply with health codes. They conduct regular inspections and follow up on complaints or violations to safeguard public health.
3. What happens during a restaurant health inspection?
During a health inspection, inspectors assess various aspects of restaurant operations, such as:
- Food storage and preparation methods.
- Cleanliness of equipment and facilities.
- Employee hygiene practices.
- Pest control and waste management.
- Violations are noted, and restaurants may be required to address them promptly to avoid penalties or closures.
4. Is the KNOW app suitable for small restaurants or only large chains?
KNOW is designed for restaurants of all sizes. Whether you operate a single-location café or manage a chain of outlets, KNOW can help simplify operations, improve compliance, and save time, making it a valuable tool for small and large businesses alike.
5. What are the 5 basic food safety rules?
- Keep it clean: Wash hands, utensils, and surfaces regularly to prevent contamination.
- Separate foods: Avoid cross-contamination by keeping raw and cooked foods apart.
- Cook thoroughly: Ensure food reaches safe internal temperatures to kill harmful bacteria.
- Store safely: Refrigerate perishables promptly and keep foods at proper holding temperatures.
- Check for freshness: Use fresh ingredients and discard items past their expiration dates.
6. How often does a health inspector come around to conduct a health inspection?
The frequency of health inspections varies depending on the location and the type of establishment. Typically:
- High-risk restaurants (handling raw meats, dairy, etc.) may be inspected every 3 to 6 months.
- Lower-risk establishments (like coffee shops) might only be inspected annually.
Additional inspections may occur due to complaints or follow-ups on previous violations.
7. What is the lowest health score a restaurant can have?
Health inspection scores vary by region, but generally:
- A score of 70 or below (on a 100-point scale) is often considered failing in many areas.
- In such cases, the restaurant might face penalties, required corrective actions, or even temporary closure until the issues are resolved.








![The 10 Best Restaurant Scheduling Software and Apps [2025] restaurant scheduling software](https://www.getknowapp.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/restaurant-scheduling-software-360x240.png)





